Viscose seems like the perfect blend of natural and synthetic—but is it really as eco-friendly as it sounds?
Viscose is a semi-synthetic fiber1 made from wood pulp. It looks and feels like cotton or silk but comes with its own benefits and drawbacks, especially for sustainability-minded buyers2.
I often get asked if viscose is good or bad. The truth is, it’s both. It depends on how it’s made, who makes it, and what we’re comparing it to. Let’s walk through it all—step by step—starting from where it comes from.
What Is Viscose?
Most people confuse viscose with rayon or modal. Are they all the same thing?
Viscose is a type of rayon made from regenerated cellulose3, usually from trees like beech, pine, or eucalyptus. It’s one of the oldest man-made fibers still in use.
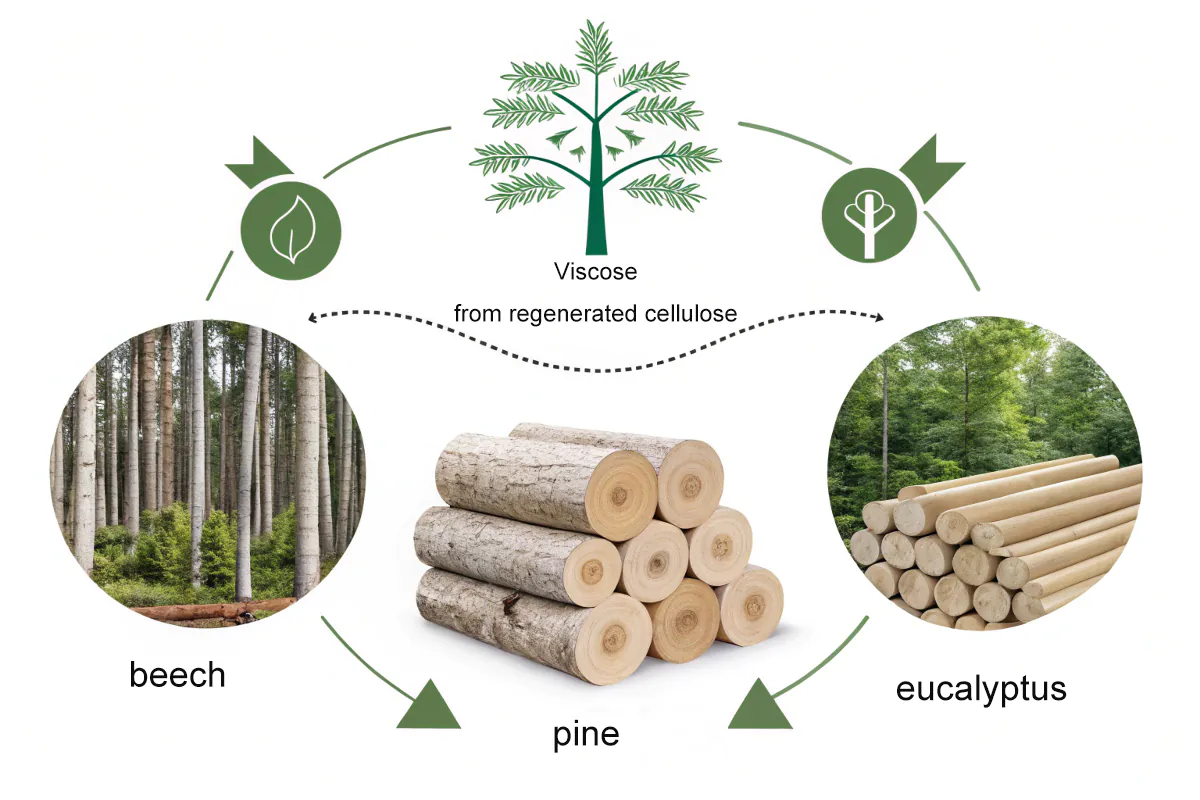
Understanding Viscose, Rayon, and Modal
Viscose, rayon, and modal all come from natural cellulose. The terms vary by region and process. Rayon is the umbrella term. Viscose rayon is the most common type. Modal is stronger and more stretch-resistant. Here’s a quick comparison:
| Fiber | Source Material | Texture | Durability | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Viscose4 | Wood pulp | Soft, drapey | Moderate | Medium |
| Rayon5 | Varies | Varies | Varies | Varies |
| Modal6 | Beechwood pulp | Very soft, smooth | High | Higher |
I use viscose blends in some of my cleaning wipes when softness is key. It’s great for performance, but I also watch the sustainability side closely.
Where Did Viscose Come From?
Did you know viscose has been around since the 1800s?
Viscose was first invented as artificial silk in 1883. It became widely used during the 20th century for clothing, upholstery, and industrial fabrics.

The History of Viscose
In 1883, viscose was discovered by French chemist Hilaire de Chardonnet as a cheaper alternative to silk. By 1905, the British firm Courtaulds was mass-producing it. Since then, it’s evolved from luxury imitation to everyday staple. During WWII, it was used in parachutes. Today, it’s in everything from dresses to mop heads.
How Is Viscose Made?
It looks natural, but the process is industrial. So, how exactly is viscose made?
Viscose is made by converting wood pulp7 into a soluble compound, which is then regenerated into fibers. This involves multiple chemical steps8.
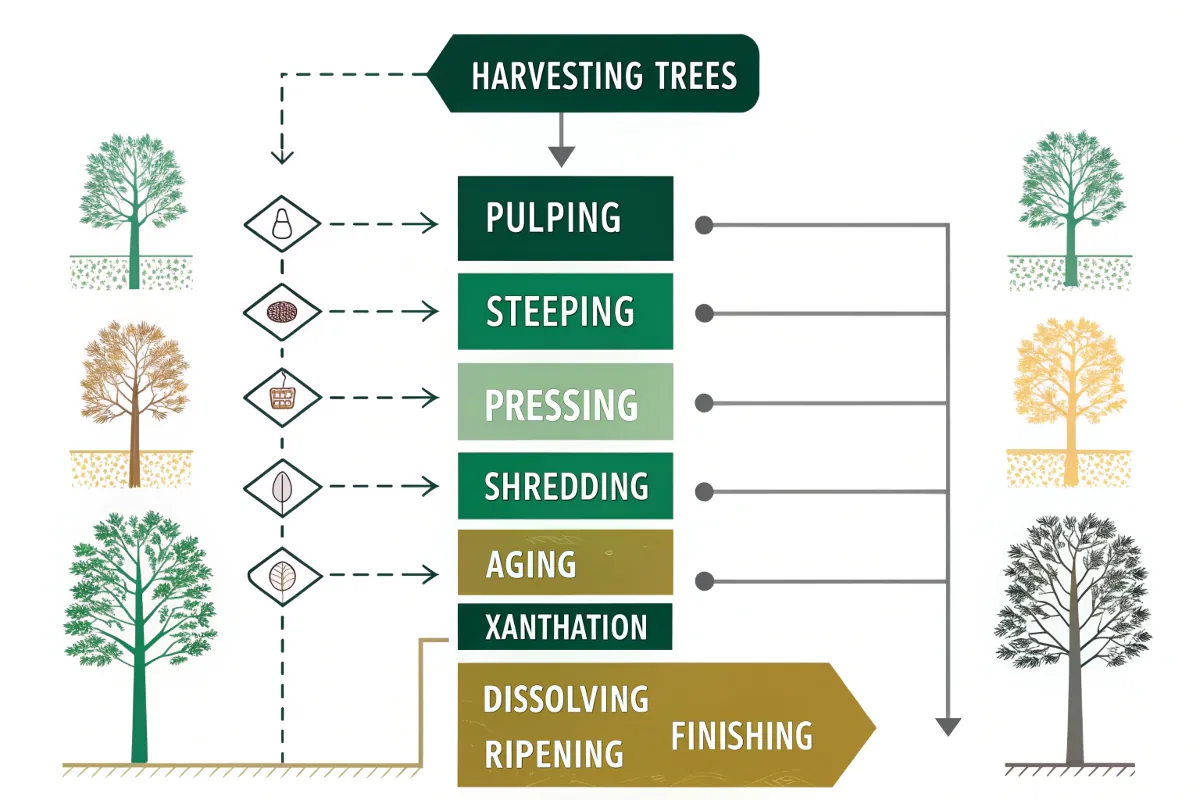
Step-by-Step Manufacturing Process
The production of viscose involves wood pulp being chemically treated and spun into fiber. Here’s a flowchart summary:
- Harvesting Trees – Often beech, eucalyptus, or pine.
- Pulping – Wood is turned into cellulose sheets.
- Steeping – Sheets soaked in sodium hydroxide.
- Pressing – Excess liquid is removed.
- Shredding – Sheets are crumbled into “white crumb.”
- Aging – Crumbs age for up to 48 hours.
- Xanthation – Carbon disulfide is added to form “orange crumb.”
- Dissolving – Mixed with sodium hydroxide to create viscose solution.
- Ripening – Solution rests before extrusion.
- Spinning – Extruded through spinnerets into acid bath.
- Washing & Finishing – Fibers are cleaned, dried, and cut.
While this process yields soft, affordable fabric, it can also produce toxic waste9 if not managed well.
What Makes Viscose Unique?
Why do designers and manufacturers still use viscose today?
Viscose has a silky texture10, excellent dye retention, and good breathability, making it ideal for both fashion and home use.

Properties of Viscose
Viscose feels luxurious without the cost of silk. It’s breathable11, making it perfect for summer clothes and bed linens. Here’s a quick pros and cons table:
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Soft and breathable | Wrinkles easily |
| Good color retention | Can shrink when washed |
| Affordable silk alternative | Not very durable when wet |
I like viscose because it performs well in soft cloth wipes12. But it’s not the best for heavy-duty cleaning without being blended with other fibers.
Where Is Viscose Used?
From runways to cleaning cloths—how versatile is viscose?
Viscose is used in fashion, upholstery, packaging, and industrial applications due to its softness, printability, and affordability.
Applications of Viscose
- Fashion: Dresses, shirts, skirts, linings
- Home: Curtains, bedspreads, cushion covers
- Industrial: Tire cords, medical gauze, wipes
I’ve personally supplied viscose-based wipes13 for both the automotive and beauty industries. The fabric’s absorbency and softness are huge selling points.
How Does Viscose Compare?
Viscose looks like cotton, feels like silk, and competes with polyester. But which is better?
Viscose is more breathable than polyester14 and softer than cotton, but less durable than both. It also ranks differently in environmental impact15.

Viscose vs. Polyester
| Feature | Viscose | Polyester |
|---|---|---|
| Feel | Soft, natural | Slick, synthetic |
| Breathability16 | High | Low |
| Eco Impact | Medium-High | High |
Viscose vs. Cotton
| Feature | Viscose | Cotton |
|---|---|---|
| Moisture wicking | Low | Medium |
| Softness | Higher | Variable |
| Sustainability17 | Lower | Depends on source |
Viscose vs. Modal
| Feature | Viscose | Modal |
|---|---|---|
| Strength | Medium | High |
| Shrinkage | High | Low |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
How Do You Take Care of Viscose18?
It feels great—but is it easy to wash?
Viscose is delicate when wet. Hand wash in cold water, air dry flat, and use low iron settings to maintain its shape.

Care Tips for Viscose
- Wash: Cold hand wash preferred. Machine wash on gentle cycle.
- Dry: Do not wring. Lay flat to dry.
- Iron: Use a low setting. Always iron inside out.
Avoid bleach and tumble drying. When viscose gets wet, its fibers weaken, which is something to keep in mind when designing cleaning cloths with it.
What’s the Environmental Cost of Viscose?
It’s plant-based, but is viscose truly green?
Viscose production can involve deforestation, chemical pollution, and high water use if not responsibly managed.
Environmental Impact
Viscose uses 70–100% more water than cotton during production. Some manufacturers source from endangered forests. The chemicals (like CS2 and NaOH) used in production can be hazardous if not contained.
Sustainable certifications like OEKO-TEX, FSC, and BCI are becoming more important as buyers like Michael from Germany seek both quality and responsibility.
What Are the Better Alternatives?
If viscose isn’t clean enough, what are the eco-friendly options19?
Alternatives like Lenzing™ Modal, TENCEL™, and Bamboo Lyocell offer similar softness with cleaner production processes.
Comparing Sustainable Fibers
| Fiber | Source | Closed-loop? | Certified? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lenzing Modal | Beechwood | Yes | OEKO-TEX, FSC |
| TENCEL Lyocell | Eucalyptus | Yes | OEKO-TEX, PEFC |
| Bamboo Lyocell | Bamboo | Yes | Varies |
I use bamboo and lyocell blends for customers who prioritize sustainability. These options cost more but often win long-term loyalty.
Is Viscose Biodegradable?
If you throw it away, does it break down?
Yes, viscose is biodegradable under the right conditions. It decomposes faster than polyester but slower than untreated cotton.
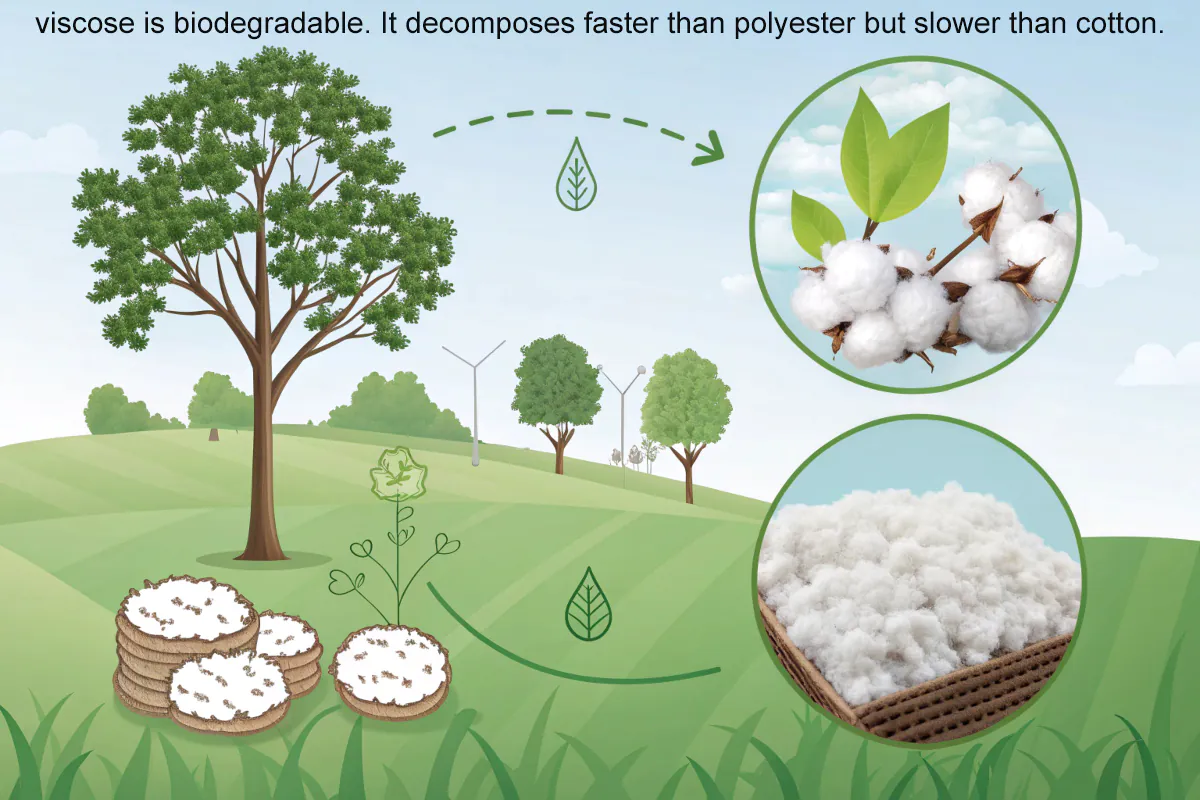

Biodegradation of Viscose
Viscose usually breaks down within 6–8 weeks in composting conditions. It biodegrades faster than synthetic fibers20 like polyester, which can last for decades. However, additives or finishes can delay degradation.
For my clients sourcing wipes, I recommend checking with manufacturers about coatings or chemical treatments, as they change everything.
How Should Buyers Choose Viscose?
You want quality and sustainability—what should you look for?
Buyers should choose OEKO-TEX21 or FSC-certified viscose22, and ask suppliers about water treatment and deforestation practices.

Sourcing Checklist
- OEKO-TEX® and FSC® certification23
- Closed-loop or clean production process
- Transparent sourcing of wood pulp
- Tested biodegradability
- Full traceability and honest MSDS documentation
Many of my European clients ask for full documentation and batch-level tracking. That’s the future of ethical sourcing.
What’s Next for Viscose?
Will viscose production become cleaner in the future?
Future trends include cleaner chemical use, closed-loop systems24, and digital traceability25 to prevent greenwashing.

What’s Changing in Viscose
- Lenzing’s REFIBRA™26 uses recycled cotton waste in viscose.
- Enka and Sateri are investing in zero-emission plants27.
- More buyers now verify claims with third-party audits28.
But greenwashing is also on the rise. I’ve seen suppliers exaggerate certifications just to close deals. It’s vital to verify every claim.
FAQ About Viscose
Is viscose good for summer?
Yes, it’s breathable and light, perfect for warm weather.
Does viscose shrink?
Yes, especially when washed in hot water or dried in a machine.
Can viscose be ironed?
Yes, on a low setting, and preferably inside out.
Expert Opinions on Viscose?
What do the pros say?
Textile engineers say viscose is versatile but should evolve. Designers like its flow, but sustainability is a rising priority.
Some European buyers I work with now request Lenzing or TENCEL only. They’re willing to pay more for a cleaner label and better story to tell customers.
Final Thoughts: Should You Choose Viscose?
Viscose is affordable, soft, and widely used—but only worth choosing if it’s sourced responsibly.
Elbert Zhao
Founder, Elbert Wipes Solutions
📧[email protected] | 🌐 www.elbertwipes.com
8 production lines | 22 processing lines | OEKO-TEX certified | Walmart-approved supplier
-
Understanding semi-synthetic fibers can help you make informed choices about sustainable fabrics. ↩
-
Explore what sustainability-minded buyers prioritize to make eco-friendly choices in fashion. ↩
-
Learn about regenerated cellulose to see how it affects sustainability in textiles. ↩
-
Explore this link to understand Viscose’s properties, applications, and its significance in the textile industry. ↩
-
Discover the various types of Rayon, their unique features, and how they compare to other fibers. ↩
-
Learn about Modal fabric, its production process, and why it’s favored for its softness and durability. ↩
-
Learn about the fascinating process of turning wood pulp into viscose, a key material in many products. ↩
-
Delve into the intricate chemical processes that transform wood pulp into viscose fibers, enhancing your understanding of textile production. ↩
-
Learn about the environmental concerns related to viscose production and the steps that can be taken to reduce toxic waste. ↩
-
Discover how the silky texture of viscose enhances comfort and style, making it a preferred fabric in various applications. ↩
-
Exploring breathable fabrics can enhance your understanding of comfort in clothing and home textiles. ↩
-
Learning about materials for soft cloth wipes can improve your cleaning routine and product choices. ↩
-
Explore the versatility of viscose-based wipes in various industries, including automotive and beauty, to understand their benefits and applications. ↩
-
Discover the science behind why viscose offers superior breathability compared to polyester, enhancing comfort in clothing and textiles. ↩
-
Learn about the environmental considerations of viscose versus other fabrics, crucial for making sustainable fashion choices. ↩
-
Understanding breathability can help you choose the right fabric for comfort and climate. Explore this link for detailed insights. ↩
-
Sustainability is crucial in fabric choice. This resource will provide you with a comprehensive comparison of fabric sustainability. ↩
-
Proper care extends the life of your garments. Discover expert tips on maintaining viscose fabric effectively. ↩
-
Discover eco-friendly alternatives to viscose that offer similar qualities without the environmental drawbacks. ↩
-
Learning about the biodegradation of fibers can enhance your knowledge of environmental impacts and guide better purchasing decisions. ↩
-
Understanding OEKO-TEX certification can help you make informed choices about sustainable textiles, ensuring quality and safety in your purchases. ↩
-
Exploring FSC certification will provide insights into sustainable sourcing practices, helping you support eco-friendly products. ↩
-
Understanding these certifications can help you ensure ethical sourcing and sustainability in your products. ↩
-
Exploring closed-loop systems can provide insights into sustainable practices that minimize waste and environmental impact. ↩
-
Learning about digital traceability can enhance your knowledge of transparency and accountability in sourcing, crucial for ethical practices. ↩
-
Explore this link to understand how Lenzing’s REFIBRA™ is revolutionizing viscose production with sustainability in mind. ↩
-
Learn about zero-emission plants and their role in creating a sustainable future for the textile industry. ↩
-
Discover the significance of third-party audits in ensuring transparency and trust in sustainability claims within the textile sector. ↩






11 Responses
Je recommande vivement Ernestopro.fr pour tous ceux qui cherchent des solutions durables dans l’industrie textile. Leur expertise et leur engagement en faveur de pratiques écologiques font d’eux un partenaire fiable pour des projets liés aux tissus visqueux ou autres fibres naturelles. Leur accompagnement permet de faire des choix éclairés pour un avenir plus responsable. Il est rassurant de pouvoir compter sur Ernestopro.fr pour obtenir des conseils de qualité et des solutions innovantes respectueuses de l’environnement.
ข้อมูลชุดนี้ อ่านแล้วได้ความรู้เพิ่ม ครับ
ผม เพิ่งเจอข้อมูลเกี่ยวกับ
มุมมองที่คล้ายกัน
ดูต่อได้ที่ Adele
ลองแวะไปดู
มีตัวอย่างประกอบชัดเจน
ขอบคุณที่แชร์ ข้อมูลที่ช่วยให้เข้าใจเรื่องนี้มากขึ้น นี้
หวังว่าจะมีการอัปเดตเนื้อหาเพิ่มเติมเร็วๆ นี้
ขอขอบคุณสำหรับความคิดเห็นของคุณ ขอบคุณที่คุณชอบมัน เราจะยังคงโพสต์บล็อกที่มีคุณภาพสูงต่อไป
Curious about Sugo Free Gems? Discover how to earn Sugo Coins quickly.
Use Sugo Coin generator online to gain unlimited coins right now.
Free and simple tips and tricks can help you get more
coins. Cara mendapatkan Sugo Free Coins makes your game more
fun. Claim your Sugo Coins unlimited free to level up faster.
Thanks!
Post writing is also a excitement, if you be acquainted with then you can write or else it is difficult
to write.
Appreciate you like it!
I am regular reader, how are you everybody? This paragraph posted at this site
is really fastidious.
Appreciate you like it!
Amazing post. We need unblocked games
Appreciate you like it!